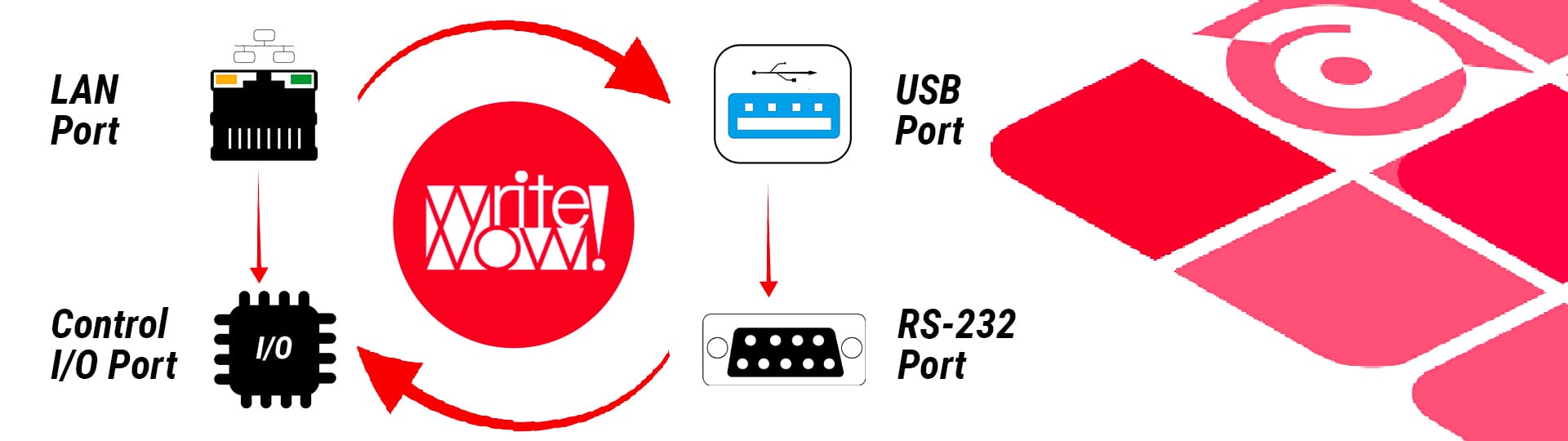
 It is fundamental that this port is natively present in the programmer in order to be connected inside a local LAN network together with other devices.
It is fundamental that this port is natively present in the programmer in order to be connected inside a local LAN network together with other devices.
One of the main advantages of a LAN port is that it can be connected to the Internet and can control in this way the programming system remotely.
Another advantage of the LAN system, is that more programming units can be connected to the PC (to create multiple and mixed solutions) with fast data and file transfer and with a very high reliability in the communication.  The standard USB was thought to enable an easy installation of the peripheral (programmer) with its Plug and Play functionalities such that it has definitivily replaced the RS232 serial port and the parallel port during the years.
The standard USB was thought to enable an easy installation of the peripheral (programmer) with its Plug and Play functionalities such that it has definitivily replaced the RS232 serial port and the parallel port during the years.
The USB port can also work in “Virtual COM” mode; in this way the USB port of the programmer is recognised by the PC as a serial interface but not limited by the serial’s baudrate. The use of the Virtual COM enables the compatibility between the classic serial program and the modern equipment.
 The COM/RS-232 port has been replaced by the USB, a more modern method which doesn’t require a specific knowledge for its implementation. However, if the programming system is connected to an embedded system (eg, Arduino, Raspberry) the communication port RS-232 represents nowadays the easiest interfacing solution.
The COM/RS-232 port has been replaced by the USB, a more modern method which doesn’t require a specific knowledge for its implementation. However, if the programming system is connected to an embedded system (eg, Arduino, Raspberry) the communication port RS-232 represents nowadays the easiest interfacing solution.
 In the 80s/90s it used to symbolise a possible communication choice with a peripheral (the printer) which allowed to reach a faster data transfer than a serial RS-232 port. Today the parallel port is no longer used and we discourage its use.
In the 80s/90s it used to symbolise a possible communication choice with a peripheral (the printer) which allowed to reach a faster data transfer than a serial RS-232 port. Today the parallel port is no longer used and we discourage its use.
 This interfacing mode allows to control the programmer through I/O signals. Typically, the programming cycle is activated by a START signal; the programmer signals with BUSY the execution state and then with an OK/ERR (PASS/FAIL) signal it shows the result.
This interfacing mode allows to control the programmer through I/O signals. Typically, the programming cycle is activated by a START signal; the programmer signals with BUSY the execution state and then with an OK/ERR (PASS/FAIL) signal it shows the result.
This interfacing method is used when the system is connected to an embedded system lacking of communication ports or simply when the Testing Engineer prefers to interface the programming system to the ATE mashine with simple I/O rather than using the serial communication ports.
The WriteNow! hardware programming platform developed by Algocraft, supports the following communication ports: LAN, USB, RS232 and CONTROL I/O offering in this way the maximum flexibility for the interface with a host system.